티스토리 뷰
반응형
해시
- 해싱 (hashing)
- 해시 함수 (hash function)
- 해시 테이블 (hash table)
- 구현 (C++)

🧐 해싱 (hashing)
해싱은 유사한 개체 그룹에서 특정 개체를 고유하게 식별하는 데 사용되는 기술로, 키(key)에 산술적인 연산을 적용하여 항목이 저장되어 있는 테이블의 주소를 계산하여 항복에 접근한다.

위 그림은 키(key)를 이용하여 해시 함수를 통해 항목에 접근하는 과정을 나타낸 것이다.
위와 같은 탐색 과정을 해싱(hashing)이라고 한다.
🧐 해시 함수 (hash function)
해시 함수는 임의의 데이터를 고정된 길이로 매핑하는 함수를 말한다.
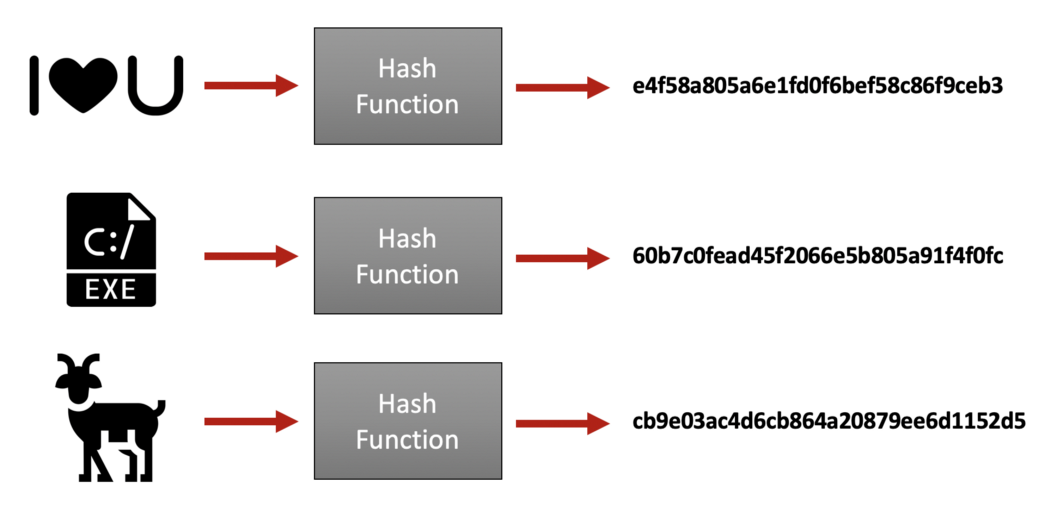
데이터에 해싱 작업이 적용되면 원래 데이터를 다시 가져올 수 없으므로 단방향 프로세스라고도 한다.
또한 모든 해시 출력은 고유한 입력에 대해 고유하고 동일한 입력에 대해 동일하다는 특징이 있다.
🧐 해시 테이블 (hash table)
해시 테이블은 해싱을 통해 매핑된 키(key)와 값(value)으로 이루어진 자료구조를 말한다.
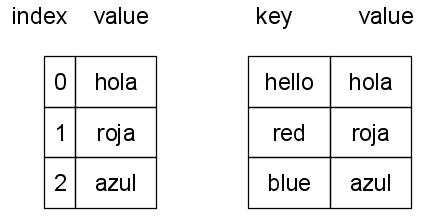
🧐 구현 (C++)
- HashFunc(int k) : 해시 함수
- Insert(int k, int v) : key와 value 추가
- SearchKey(int k) : key 찾기
- Remove(int k) : 해당 값 삭제
클래스 생성
const int T_S = 200;
class HashTableEntry
{
public:
int k;
int v;
HashTableEntry(int k, int v)
{
this->k = k;
this->v = v;
}
};
class HashMapTable
{
private:
HashTableEntry **t;
public:
HashMapTable();
int HashFunc(int k);
void Insert(int k, int v);
int SearchKey(int k);
void Remove(int k);
};
생성자 초기화
HashMapTable::HashMapTable()
{
t = new HashTableEntry *[T_S];
for (int i = 0; i < T_S; i++)
{
t[i] = NULL;
}
}
HashFunc 함수
int HashMapTable::HashFunc(int k)
{
return k % T_S;
}
Insert 함수
void HashMapTable::Insert(int k, int v)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL && t[h]->k != k)
{
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] != NULL)
delete t[h];
t[h] = new HashTableEntry(k, v);
}
SearchKey 함수
int HashMapTable::SearchKey(int k)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL && t[h]->k != k)
{
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] == NULL)
return -1;
else
return t[h]->v;
}
Remove 함수
void HashMapTable::Remove(int k)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL)
{
if (t[h]->k == k)
break;
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] == NULL)
{
cout << "No Element found at key " << k << "\n";
return;
}
else
{
delete t[h];
}
cout << "Element Deleted\n";
}
📌 전체 코드
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int T_S = 200;
class HashTableEntry
{
public:
int k;
int v;
HashTableEntry(int k, int v)
{
this->k = k;
this->v = v;
}
};
class HashMapTable
{
private:
HashTableEntry **t;
public:
HashMapTable();
int HashFunc(int k);
void Insert(int k, int v);
int SearchKey(int k);
void Remove(int k);
};
HashMapTable::HashMapTable()
{
t = new HashTableEntry *[T_S];
for (int i = 0; i < T_S; i++)
{
t[i] = NULL;
}
}
int HashMapTable::HashFunc(int k)
{
return k % T_S;
}
void HashMapTable::Insert(int k, int v)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL && t[h]->k != k)
{
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] != NULL)
delete t[h];
t[h] = new HashTableEntry(k, v);
}
int HashMapTable::SearchKey(int k)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL && t[h]->k != k)
{
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] == NULL)
return -1;
else
return t[h]->v;
}
void HashMapTable::Remove(int k)
{
int h = HashFunc(k);
while (t[h] != NULL)
{
if (t[h]->k == k)
break;
h = HashFunc(h + 1);
}
if (t[h] == NULL)
{
cout << "No Element found at key " << k << "\n";
return;
}
else
{
delete t[h];
}
cout << "Element Deleted\n";
}
int main()
{
HashMapTable hash;
int k, v;
int c;
while (1)
{
cout << "1.Insert element into the table\n";
cout << "2.Search element from the key\n";
cout << "3.Delete element at a key\n";
cout << "4.Exit\n===\n";
cout << "Enter your choice: ";
cin >> c;
switch (c)
{
case 1:
cout << "Enter [KEY, VALUE] : ";
cin >> k >> v;
hash.Insert(k, v);
break;
case 2:
cout << "Enter key of the element to be searched: ";
cin >> k;
if (hash.SearchKey(k) == -1)
{
cout << "No element found at key " << k << "\n";
continue;
}
else
{
cout << "Element at key " << k << " : ";
cout << hash.SearchKey(k) << "\n";
}
break;
case 3:
cout << "Enter key of the element to be deleted: ";
cin >> k;
hash.Remove(k);
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
cout << "\nEnter correct option\n";
}
}
}
참고 사이트
Fifty Shades of Malware Hashing
좋아요는 로그인하지 않아도 누를 수 있습니다!
728x90
반응형
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 그래프 (Graph) (0) | 2022.01.05 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 트리 (tree) (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| [자료구조] 큐 (queue) (0) | 2021.12.01 |
| [자료구조] 스택 (stack) (4) | 2021.11.24 |
| [자료구조] 연결 리스트 (linked list) (0) | 2021.11.18 |
댓글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- 풀이
- 프로그래머스
- 해답
- 정답
- 자바스크립트
- 문자열
- 우종정
- 운영체제
- 파이썬
- 백준
- 정렬
- JS
- Web
- 답
- OS
- 알고리즘
- 그리디
- 구현
- 정리
- CPP
- 쉽게 배우는 자바 프로그래밍
- Python
- BFS
- py
- 연습문제
- 자바
- 쉽게배우는자바프로그래밍
- java
- C++
- 쉽게배우는
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
글 보관함
